The Ultimate Guide to the Control of Stored Grain Pest
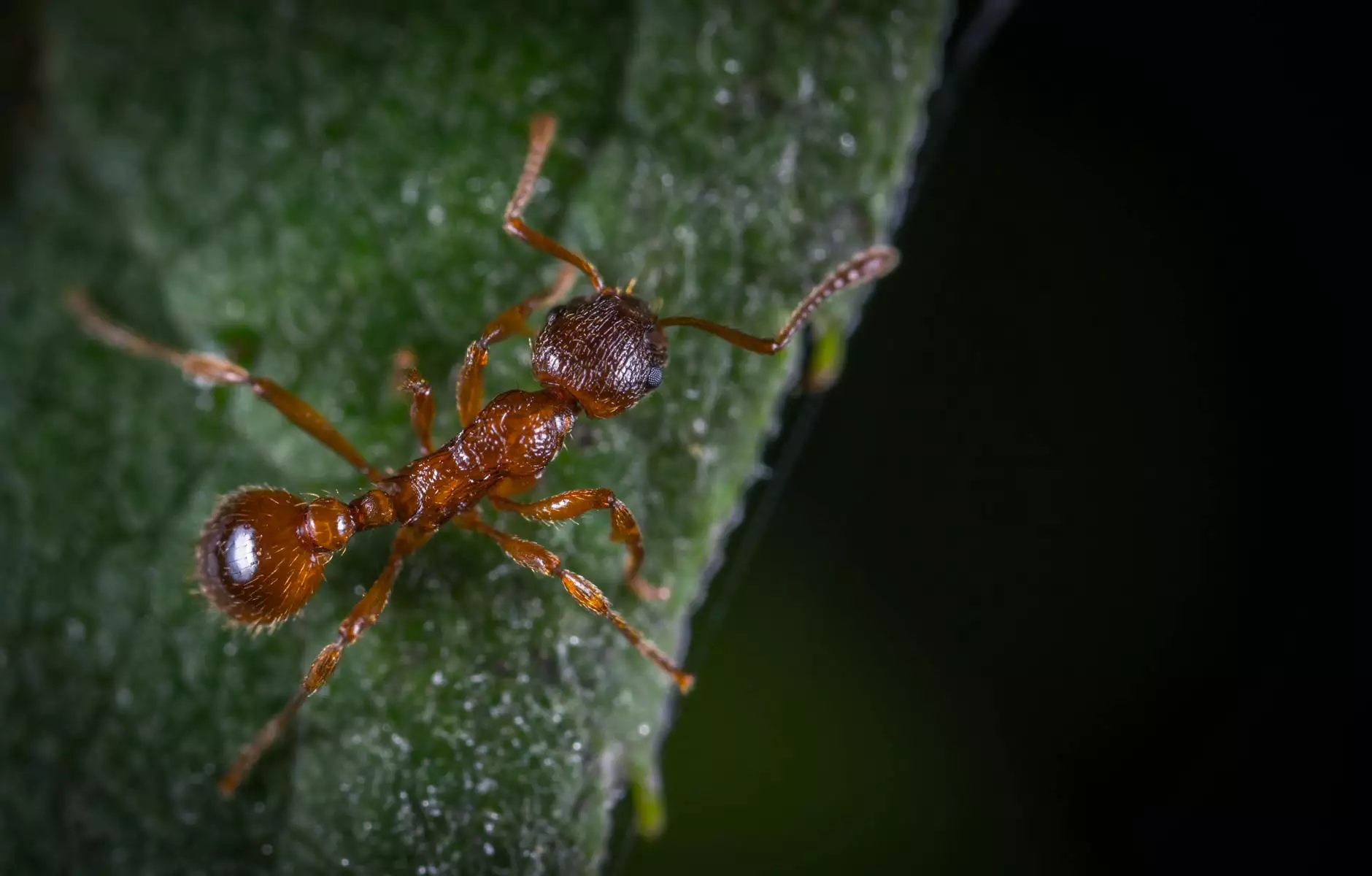

Grain storage is a vital component of the agricultural supply chain. Effective control of stored grain pest management is crucial to protect the grains from infestations that can lead to substantial financial losses. There are various types of pests that can infest stored grains, including weevils, moths, and rodents, each posing different threats to grain integrity. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various strategies, techniques, and practices for effective pest control.
Understanding Stored Grain Pests
Before implementing any control methods, it's essential to understand the types of pests that threaten your stored grains. Here are some key pests to be aware of:
- Grain Weevils: These are small, brown beetles that bore into grains, causing significant damage.
- Indian Meal Moths: These pests lay eggs that hatch into larvae, which can contaminate grains and compromise their quality.
- Rodents: Mice and rats are not only a nuisance but can consume substantial amounts of grain, leading to waste.
- Stored Grain Beetles: These beetles feed on grains and can reproduce rapidly, increasing infestations.
The Importance of Effective Pest Control
The control of stored grain pest is crucial for several reasons:
- Protection of Grain Quality: Infestations can lead to physical damage and contamination, reducing the marketability of grains.
- Economic Viability: Effective pest control reduces losses, ensuring that farmers optimize their profits.
- Health Hazards: Some pests can introduce pathogens to stored grains, which can affect consumer health.
- Long-term Sustainability: Implementing effective controls ensures the longevity of grain storage practices.
Integrated Pest Management for Stored Grains
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach that combines various strategies to control pest populations effectively while minimizing chemical usage. The following practices are integral to IPM:
1. Monitoring and Identification
Regular monitoring of grain storage facilities is essential to identify early signs of infestation. This involves:
- Using pheromone traps to capture mating adults.
- Conducting visual inspections of stored grain for signs of pest activity.
- Maintaining records of pest sightings and monitoring results.
2. Storing Grains Properly
Optimal storage conditions can reduce the likelihood of pest infestations. Consider the following:
- Temperature Control: Keep storage areas cool; pests thrive in warmer conditions.
- Moisture Control: Ensure that moisture levels are below 14% to inhibit pest growth.
- Cleanliness: Regularly clean storage facilities to eliminate any food sources for pests.
- Aeration: Utilize aeration systems to maintain dry conditions in bulk storage.
3. Use of Biological Control Agents
Biological control utilizes natural predators or pathogens to manage pest populations. Examples include:
- Nematodes: These microscopic roundworms can target pest larvae.
- Bacteria: Certain bacterial strains can reduce pest populations by causing disease in insects.
4. Chemical Control Measures
While it is vital to rely on non-chemical methods, integrating chemicals can be necessary if infestations are severe. Key considerations include:
- Choosing the right pesticide based on targeted pests.
- Following manufacturer guidelines for safe usage.
- Implementing a rotation strategy to prevent pest resistance.
5. Proper Disposal of Infested Grains
When pests infest stored grains, it's imperative for the integrity of the remaining stocks to dispose of the infested grains correctly:
- Identify the infested areas and segregate them.
- Employ methods that are environmentally safe to eliminate the pests.
- Document the process to enhance future pest management protocols.
Preventative Strategies for Grain Storage
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are effective preventative strategies for the control of stored grain pest:
Regular Maintenance of Storage Facilities
Ensure that storage facilities are well maintained. This includes:
- Patching up any holes in storage bins where pests can enter.
- Regularly inspecting the structural integrity of the storage facilities.
- Keeping the surrounding areas free of debris and tall grass where pests can harborage.
Training Staff on Pest Management Protocols
Educate your staff on the importance of pest management. Training should cover:
- Identifying signs of pest activity.
- Implementing sanitation practices.
- Understanding the lifecycle of common pests to anticipate potential outbreaks.
Embracing Technology in Pest Control
Technology plays a crucial role in improving pest control strategies. Here are a few technological advancements:
1. Smart Sensors and IoT
Integrating smart sensors into grain storage facilities can help monitor conditions real-time, ensuring:
- Temperature and moisture levels are optimal.
- Alerts are sent when pests are detected, allowing for immediate action.
2. Drones for Monitoring
Drones can provide aerial surveillance of storage facilities, allowing for:
- Identifying areas at risk of infestation due to poor storage conditions.
- Quick assessment of weather impacts on storage areas.
Conclusion
The control of stored grain pest is paramount for the success of any grain storage operation. By implementing integrated pest management strategies, embracing technology, and maintaining high standards of storage practices, farmers and grain handlers can significantly mitigate the risks associated with infestations. Utilizing these practices not only enhances grain quality and marketability but also contributes to a more sustainable agricultural system.
For those who are serious about pest control in grain storage and looking for expert advice, equipment, and service options, tsgcinc.com is your trusted partner in the field of Farm Equipment Repair and Farming Equipment. Their expertise can help maintain your grain storage facilities and implement effective pest control solutions.